Seqence Alignment (Theory)
Indentifying the similarity between sequences that may be related to functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships.
Definition
Sequence
- An arrangement of two or more related things in a successive order.
-
Related things:
- DNA (base pairs as ACTG)
- RNA (base pairs as ACUG)
- proteins (amino acids)
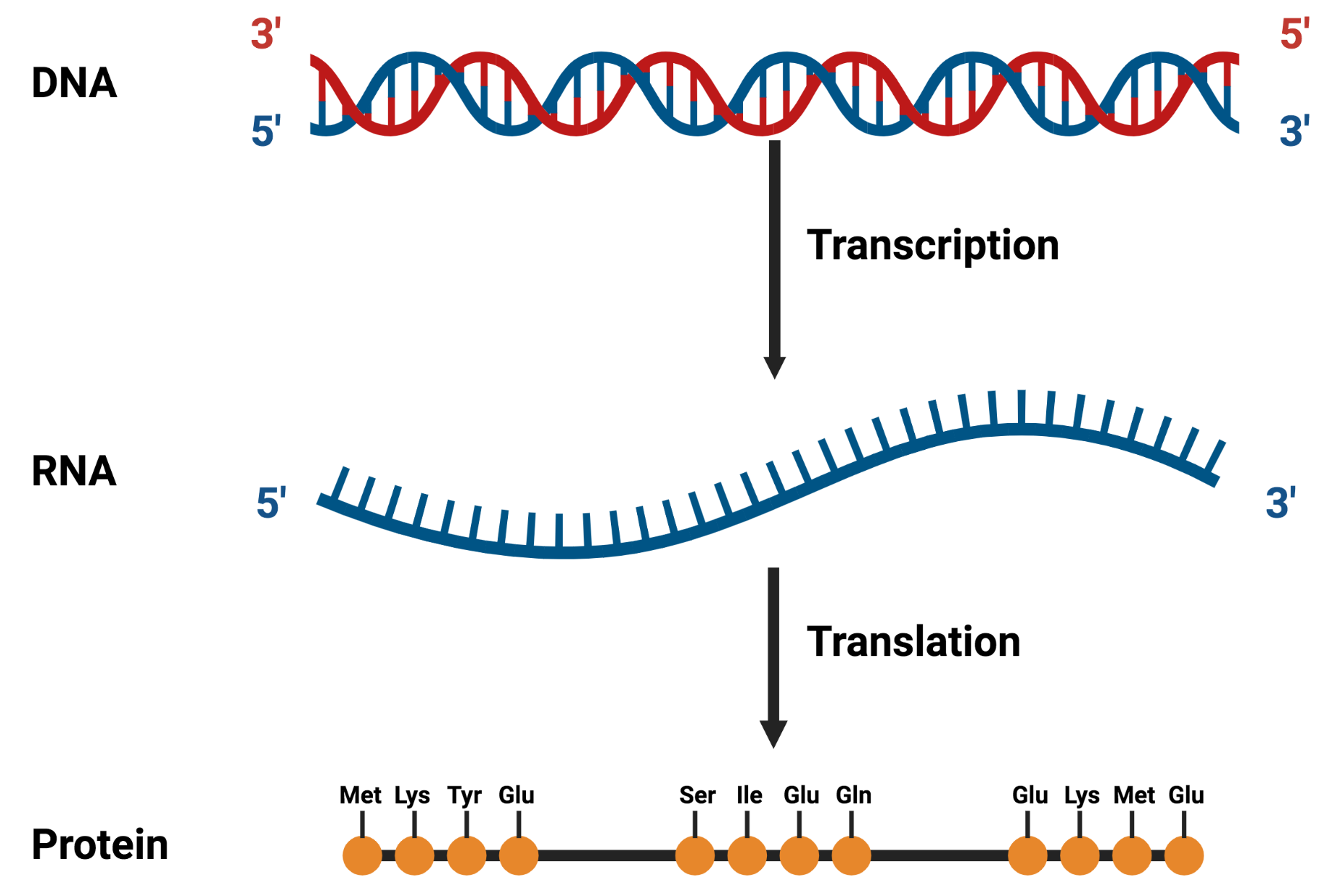
Sequence Alignment
- Arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or proteins to identify regions of similarity and identity that may be consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships.
- Probably the most important and most accomplished in bioinformatics.
- Ultimate goal: determine the similarity between different sequences.
Sequence Similarity & Sequence Indentity
- DNA & RNA: sequence similarity and sequence identity are the same.
-
Protein:
- Identity: % of exact matches between two aligned sequences.
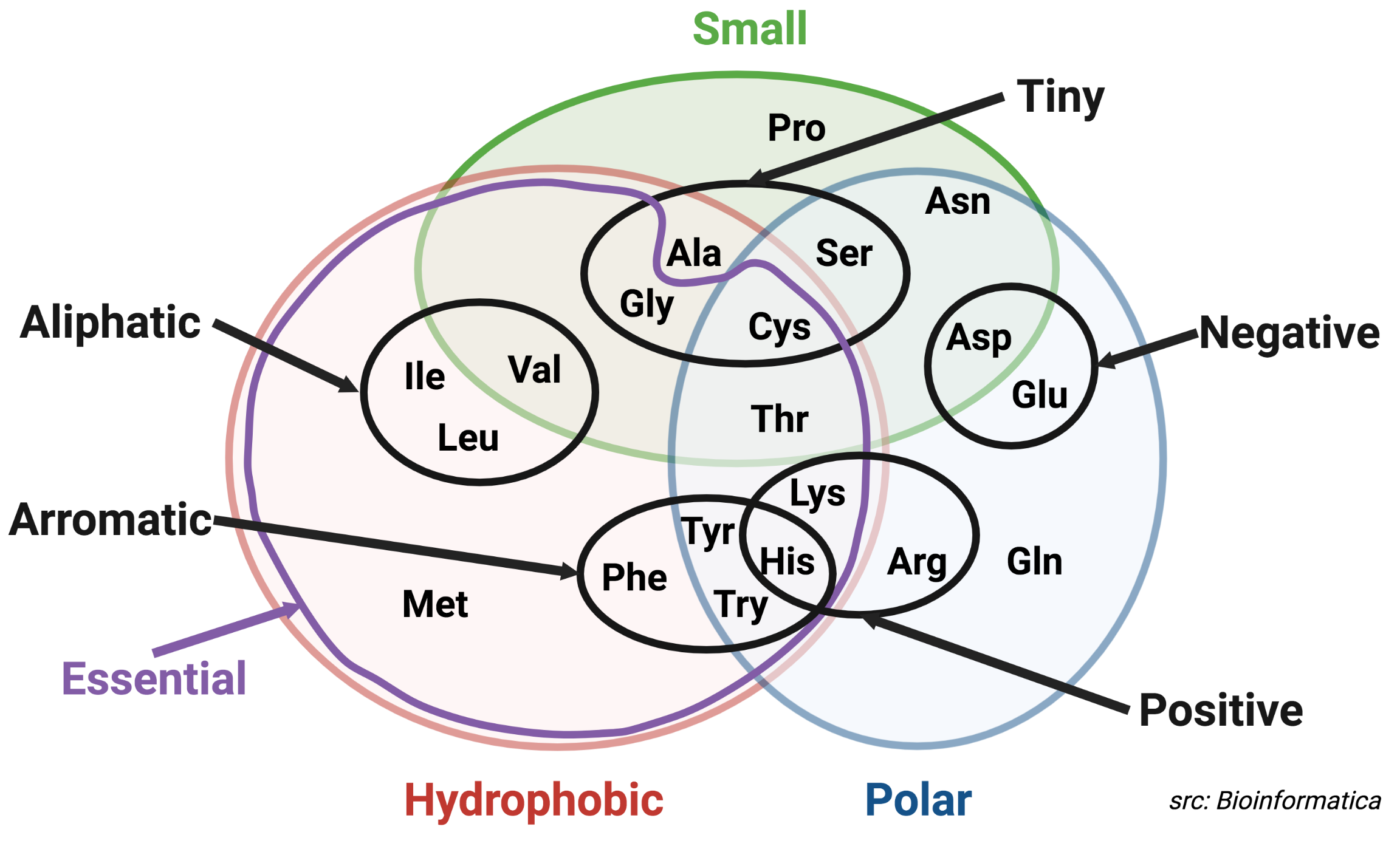
- Similarity: % of aligned residues that share similar characteristics.
Similar characteristics:
Question:
In terms of identity distance measure, if sequence A = B and B = C; then, would A be equal to C?

-
Identity(A,B) = 100%($\frac{\text{5 identical nucleotides}}{min(length(A), length(B))}$). -
Identity(B,C) = 100%($\frac{\text{5 identical nucleotides}}{min(length(B), length(C))}$). -
Identity(A,C) = 85%($\frac{\text{6 identical nucleotides}}{7}$). Therefore, 100% identity doesn’t mean two sequences are the same.
Why sequence alignment?
- Gene finding: if there is a gene in another organism with a good alignment with the open reading frame (ORF), then the ORF is likely a gene.
- Function prediction: two genes are similar determined by sequence alignment, the function of one gene is known, we can assign the same function for the other gene.
- Genome Sequence Assembly
- Indentifying homologous genes: both identity and similarity are used to deduce homology.
Interpretation
- If two sequences share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutations and gaps as indels (insertion or delection mutations)introduced in one or both lineages in the tume since they diverged from one another.
- In protein sequence alignment, the degree of similarity between amin acids occupying a partcular position in the sequence can be interpreted as a rough measure of how conserved a particular region or sequence motif is among lineages.
- the absence of substitutions or the presence of only very conservative substitutions (the substitutions of amino acids whose side chains have simiular biochemical properties) in a particular region, suggest that this region has structural or functional importance.
Algorithms
Pairwise Alignment
Dot plot
- Place one sequence on the vertical axis of a 2D grid and the other on the horizontal.
- Put dots where the two sequences match.
- Diagonal runs of dots indicate matched segments of sequences.
- Dot matrices of long sequences are often noisy –> Solution: use a window and a threshold.
- compare character by character within a window
- require certain fraction of matches within window in order to display it with a dot
- Use cases:
- Visually assessing the similarity of two protein or two nucleic acid sequences
- Finding local repeat sequences within a larger sequence by comparing a sequence to itself
Dynamic Programming
| Global Alignment | Local Alignment | |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Needleman-Wunsch | Smith-Waterman |
| Definition | Find the best posible alignment across entire length of two sequences | Find local region with highest level of similarity |
| Application | Applied to 2 closely related sequences and approximately same length | Find conserved patterns in DNA or protein sequences |
Word method
- Known as k-tuple
- heuristic methods that are not guaranteed to find an optimal alignment solution but are significantly more efficient than dynamic programming.
- Useful in large-scale database searches (FASTA and BLAST)
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
- sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences (protein, DNA, RNA)
Tools
| Priority | Tools |
|---|---|
| Speed | BLAST |
| Accurate statistics | FASTA |
| Short query sequence | GGSEARCH, GLSEARCH |
| Speed and interactive search | PSI-BLAST |
| Accurate and most prone to errors | PSI-Search |