Carbon - Chemistry & Energy
Carbon - Chemistry & Energy
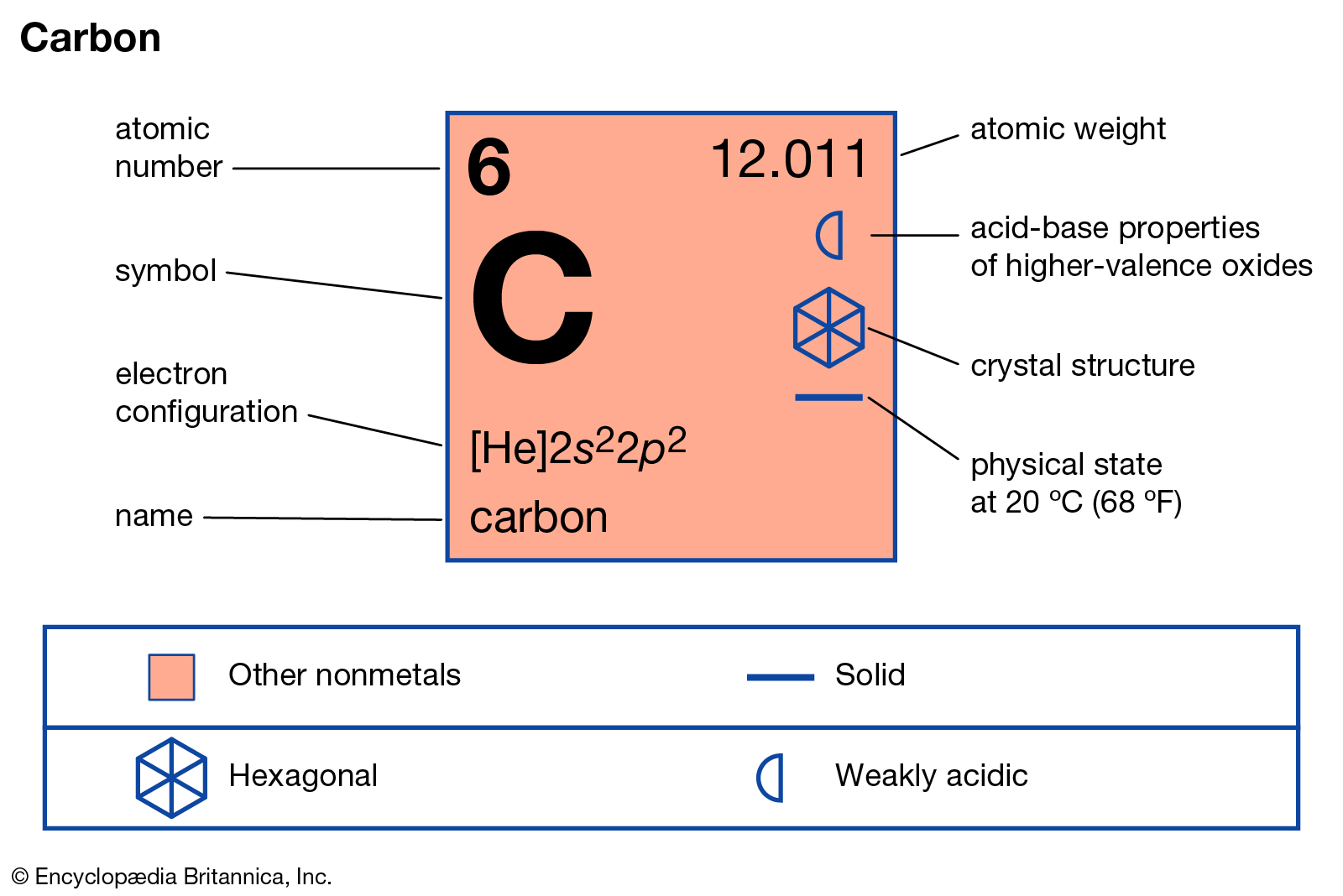
About carbon
- Foundation of biology.
-
6 proton + 6 neutron + 6 electron
-
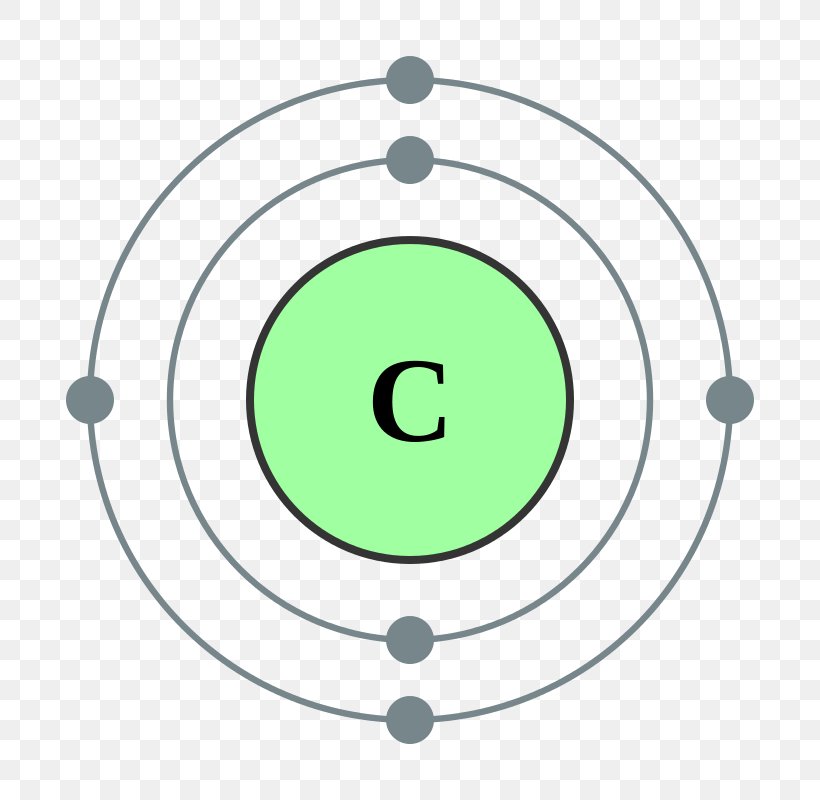
Two electron shells: 2 electrons locate on the first shell and 4 locate on the outer shell.
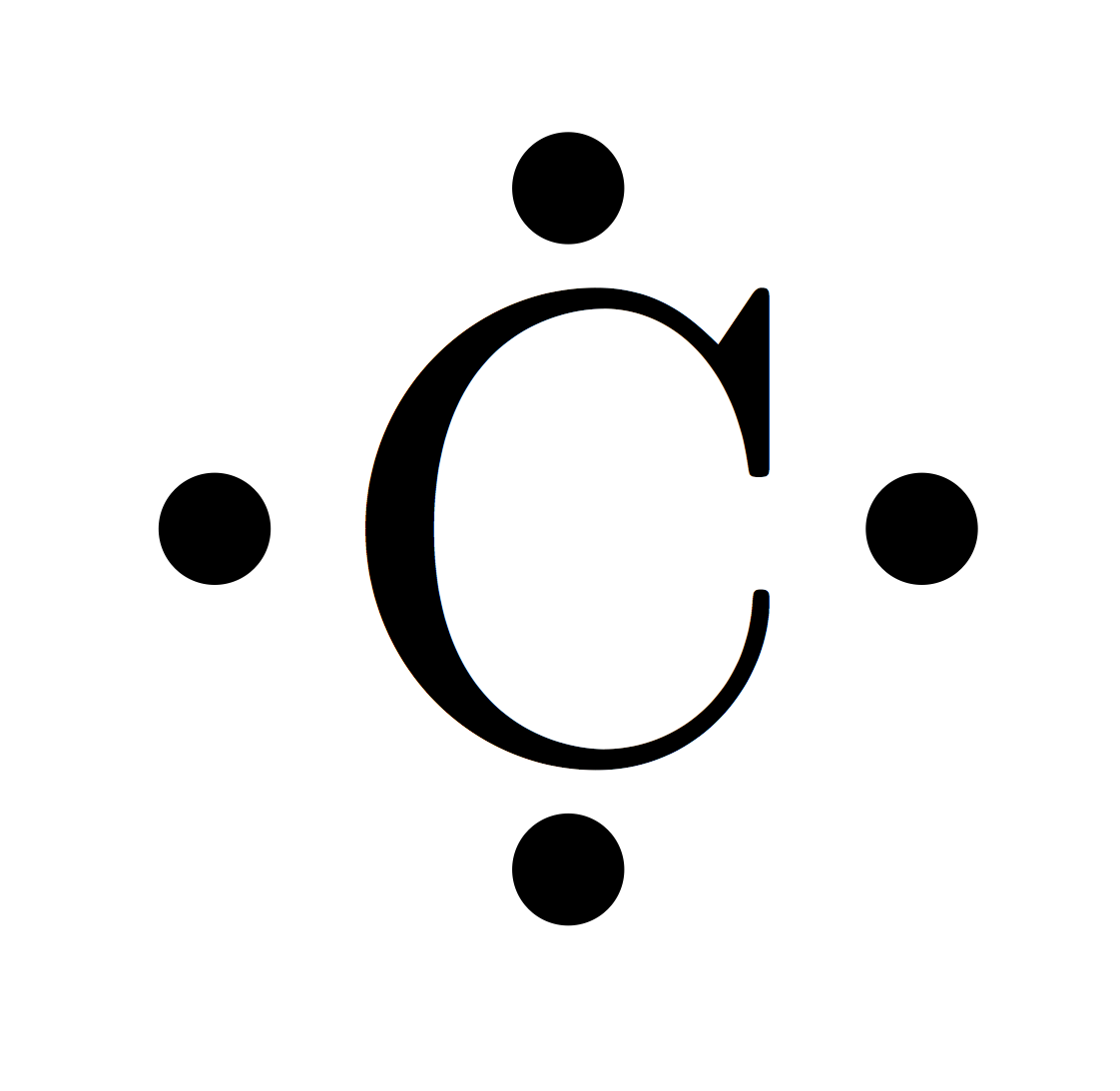
- Lewis dot structure
Gilbert Lewis
 The scientist behind these famous terms:
The scientist behind these famous terms:
- Lewis dot structure
- Valency theory
- Lewis acids and bases
Some facts about him: He was nominated 35 times for Nobel’s Prize but ended up with zero prize. What a great man!
Octet Rule
Each atom needs 8 electrons in the outer shell … to be fulfilled and happy.
This is a rule of thumb for a “happy relationship” among atoms to form a long-lasting family (molecule).
Types of bonding
Covalent bonds
When atoms share electrons with each other. Ex: $CH_{4}$, $O_{2}$, $NH_{4}$
- Non-polar covalent bond. Ex: $O_{2}$
- Polar covalent bond: there exists negative and positive pole. Ex: $NH_{4}$
Amino acids are formed by covalent bonds.
Ionic bonds
- do not share electrons
- donate or accept electrons
- live as a charged atom or ion
Alkali metals + Halogens
Examples: $NaCl$, $KF$, etc.
Hydrogen bonds
- Some molecules formed by polar covalent bonds can stick together.
- Example: $H_{2}O$
References
- Lecture: Crash course
- Britannia: Carbon chemical element